Solutions for the retail supply chain
Retail supply chain management is essential to meeting the needs of today’s omnichannel consumers. Learn more about retail supply chains and how they work. SPS Commerce helps trading partners use data to optimize every step in the supply chain.
What is a retail supply chain?
A retail supply chain is a group of companies that works together to deliver products to customers. The supply chain starts with obtaining the raw materials to make a product and continues until the final product is delivered to the end customer. The goal of retail supply chain management is to fulfill orders in the most cost-effective way while meeting customer expectations.
Each company involved in the retail supply chain is known as a trading partner. Trading partners include organizations that buy goods (retailers, grocers and distributors) and organizations that make and sell goods (manufacturers, suppliers and vendors). Organizations that store and transport goods, including third-party logistics providers and carriers, also play a key role in the retail supply chain.
Are there different types of retail supply chains?
Retail supply chains come in different shapes and sizes. Supply chains vary based on many factors, including how orders are fulfilled to the customer. Examples include:
Single Channel
A single channel supply chain fulfills orders for one selling channel. Common channels include brick-and-mortar retail, eCommerce and marketplaces.
Multichannel
A multichannel supply chain fulfills orders for more than one selling channel. Operations for each channel function in separate silos.
Omnichannel
In an omnichannel supply chain, all channels are integrated to provide a seamless experience for the customer.
How does a retail supply chain work?
Here are the steps involved in fulfilling an order in a typical retail supply chain.
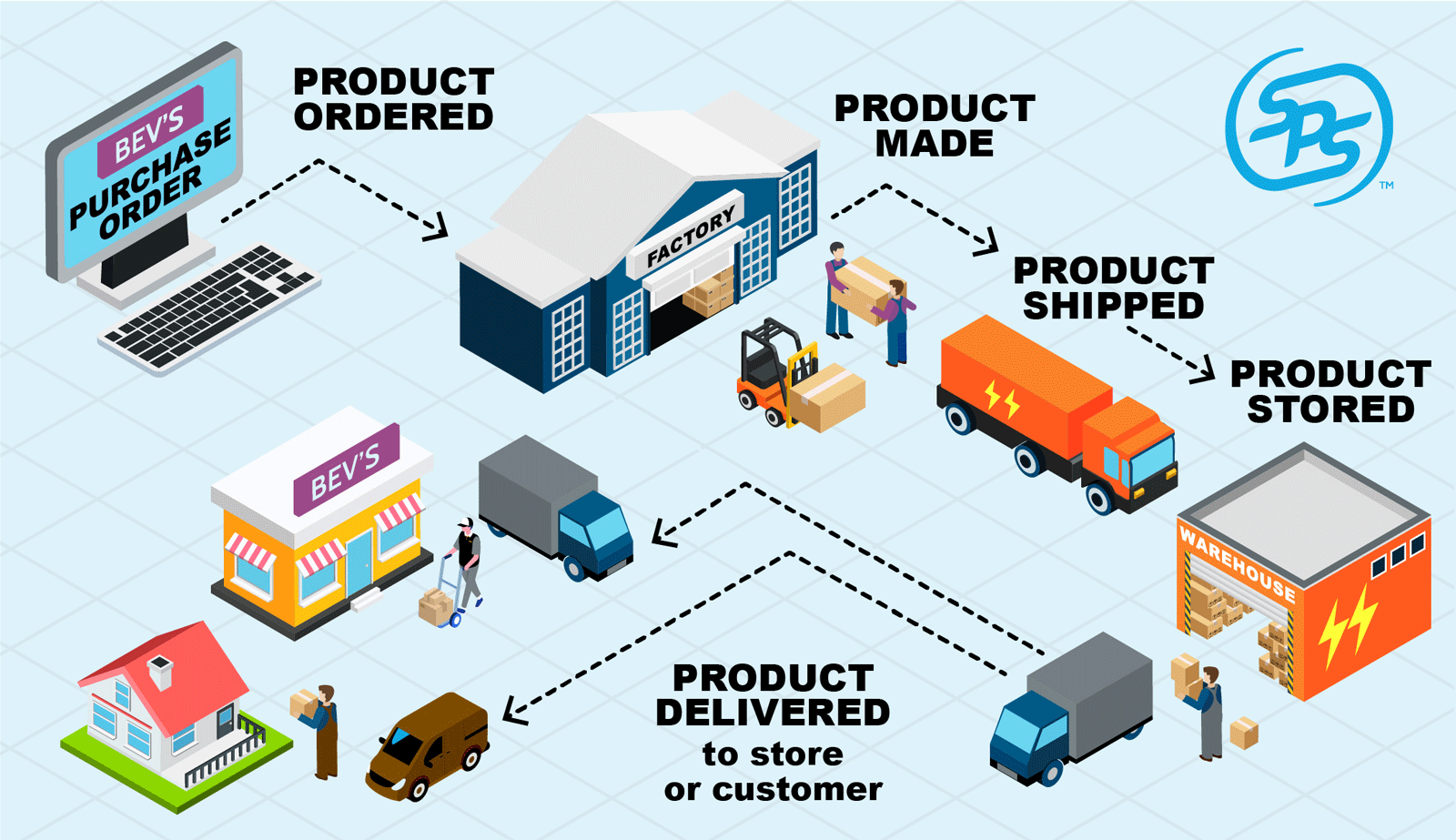
The buying organization selects which goods to purchase and which supplier to purchase the goods from. The buyer places an order for these products with their chosen supplier.
The supplier fulfills the order based on the buying organization’s requirements.
The carrier or 3PL ships the product.
The retailer receives the product in their distribution center or store.
The customer buys the product.
There are labor-intensive processes involved at each step in the retail supply chain. To ensure efficiency, each trading partner must communicate data related to the exchange of goods. Unfortunately, 91 percent of buying organizations don’t receive essential information from their suppliers. A retail network enables trading partners to more easily connect and exchange supply chain data.
Roles in the typical retail supply chain
Top supply chain challenges for retailers, grocers and distributors
Retailers, grocers and distributors are buying organizations. They send orders to suppliers or vendors, and sell these goods through stores, eCommerce, marketplaces or other channels.
Common challenges for buying organizations include:
Top supply chain challenges for suppliers
A supplier or vendor sells goods and services to another organization for them to distribute to consumers or businesses.
Top supply chain challenges for 3PLs and logistics providers
A logistics provider handles warehouse storage and fulfillment services or transportation services.
Common challenges for logistics providers include:
Retail trading partners work together to deliver a product to the end customer.

To meet the needs of today’s omnichannel customer, trading partners must share essential information about items, inventory, orders, shipments and more. This collaboration ensures customers can buy the product they want, in the channel of their choice and in their desired timeframe.
Retail supply chain solutions from SPS Commerce
SPS Commerce makes it easy for retail supply chain partners to connect and collaborate. Our cloud-based solutions help 50,000 subscribing customers around the globe improve efficiency and better serve their customers.