EDI 823 format
The EDI 823 is similar to a detailed bank statement for businesses. It provides a comprehensive overview of their financial transactions, helping them manage their cash flow, reconcile accounts and ensure accurate financial reporting.
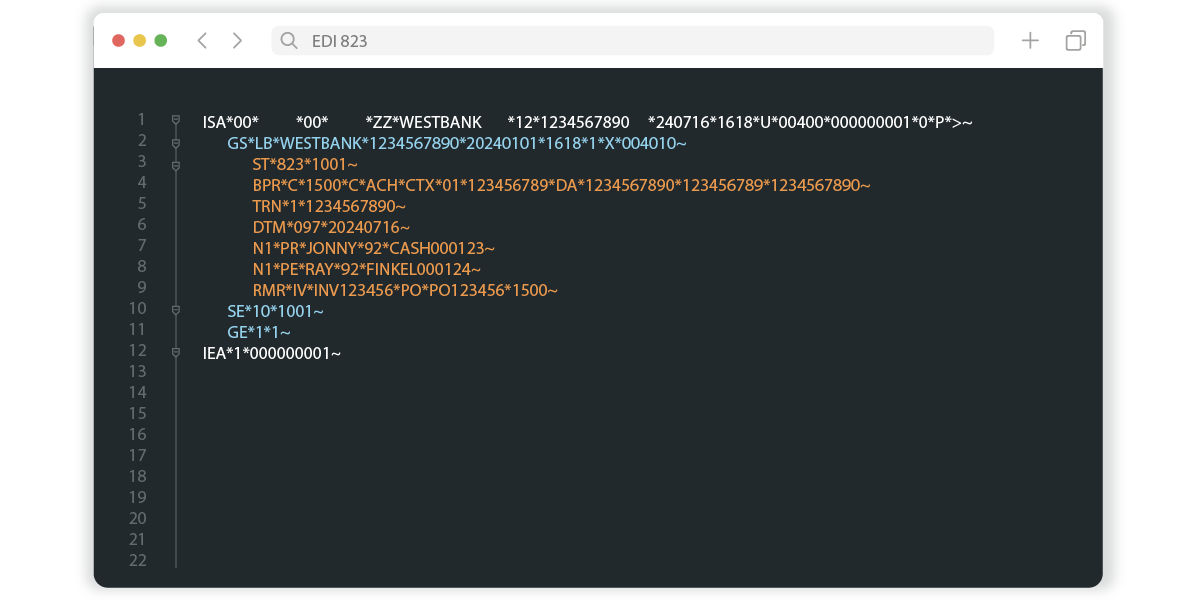
Here’s how it’s typically formatted:
ST: Transaction set header—This segment identifies the start of the transaction set and assigns a control number.
BPR: Beginning segment for payment order/remittance advice—This segment provides information about the payment order, including payment method, amount and payer details.
TRN: Trace—This segment contains trace numbers that uniquely identify the payment and remittance information.
CUR: Currency—This segment specifies the currency used for the transaction.
REF: Reference identification—This segment provides additional reference information, including invoice number or customer reference.
DTM: Date/time reference—This segment specifies dates and times relevant to the transaction, such as payment date.
N1: Name—This segment identifies the parties involved in the transaction, such as the payer and payee, using standardized codes.
N2/N3/N4: Additional name information, address, geographic location—This segment provides additional identification and location details for all parties involved.
ENT: Entity—This segment identifies the entity associated with the payment.
RMR: Remittance advice accounts receivable open item reference—This segment provides detailed information about the invoices or accounts being paid, including invoice numbers, amounts and adjustments.
DTM: Date/time reference—This segment specifies dates related to the open item references, such as invoice dates.
REF: Reference identification—This segment provides additional information related to the open item references.
ADX: Adjustment—This segment details any adjustments to the payment, such as discounts or deductions.
SE: Transaction set trailer—This segment indicates the end of the transaction set and includes the control number for verification.
How is the EDI 823 used?
The EDI 823 provides detailed remittance information that helps clients apply payments to accounts receivable accurately. This transaction set includes payment amounts, payer details and invoice numbers, ensuring that payments are correctly allocated to the corresponding invoices or accounts.
Benefits of using the EDI 823
The EDI 823 transaction set offers numerous advantages for managing financial transactions between trading partners. Here are some key benefits:
Enhanced financial reporting: Provides accurate and timely financial information, improving transparency and decision-making.
Improved cash management: Streamlines the exchange of payment data, leading to better cash flow management.
Operational efficiency: Reduces manual data entry and errors, saving time and resources.
Better reconciliation: Facilitates easier reconciliation of payments and invoices, ensuring financial records are up to date.
Compliance: Ensures adherence to industry standards and regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of non-compliance.
Stronger relationships: Enhances communication and coordination with trading partners, leading to more reliable and efficient financial transactions.
Common issues regarding the EDI 823
Data accuracy and completeness:
Accurate and complete information: Ensuring all payment and remittance details are accurate and complete to avoid misallocation of payments, reconciliation issues and disputes between trading partners.
Integration and compliance challenges:
Integration complexity: Integrating the EDI 823 with existing ERP systems can be technically challenging, requiring significant customization and leading to potential synchronization issues.
Compliance with standards: Adhering to industry-specific EDI standards and regulatory requirements demands substantial technical expertise and resources. Inconsistent implementation can lead to misinterpretations and processing errors.
Operational and security concerns:
Security concerns: Protecting sensitive payment and remittance information during transmission to prevent data breaches and unauthorized access.
Continuous monitoring and troubleshooting: Continuous monitoring and prompt troubleshooting of EDI 823 transactions are necessary to address any issues that arise.
Coordination with financial institutions: Managing relationships with multiple institutions, each potentially using different systems and standards, to prevent communication breakdowns and transactional errors.
Automate X12 EDI 823 Lockbox with Full-Service EDI from SPS Commerce
Managing ongoing EDI tasks can be complicated and time-consuming. A full-service provider, like SPS Commerce, has an knowledgeable team that handles ongoing management of your EDI solution. The SPS team actively manages 9,000 changes from retailers each year.

We work directly with your trading partners to manage connectivity, setup, requirements, updates and support efforts. We also assume ownership of understanding your trading partner requirements and making map changes.
SPS Fulfillment proactively monitors and optimizes your solution to prevent errors and minimize data entry. Interested in learning more about our EDI solution?
Additional EDI Resources
Enter a virtual library of information about EDI for suppliers, vendors and distributors to provide you with the product knowledge you need to power your business.
Ultimate List of EDI Transactions
Here are some of the most common documents and transactions that are supported through EDI automation.
Five Top EDI Documents to Automate
When you automate your most-used EDI documents, it can significantly cut down keystrokes and speed up processes.
EDI Glossary
Terminology including retail definitions, order management models, supply chain roles, software and distribution channels.
EDI for Suppliers & Vendors
Discover how leading vendor and supplier businesses are serving their customers better with EDI solutions from SPS Commerce.